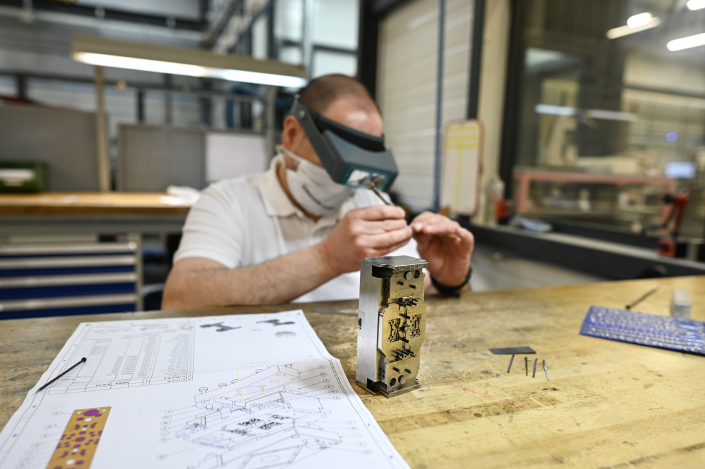
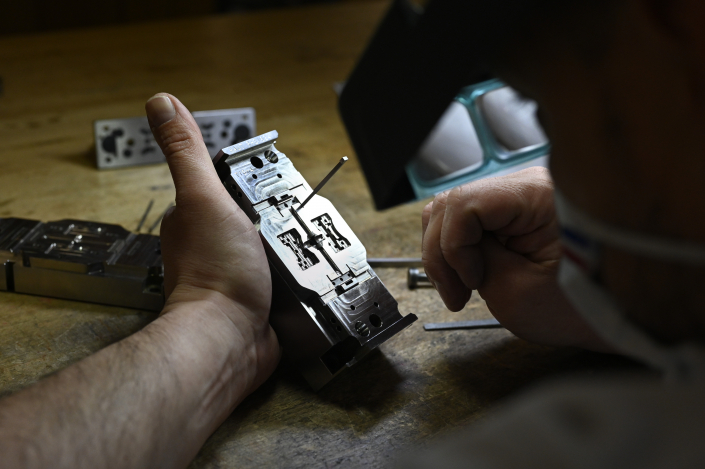
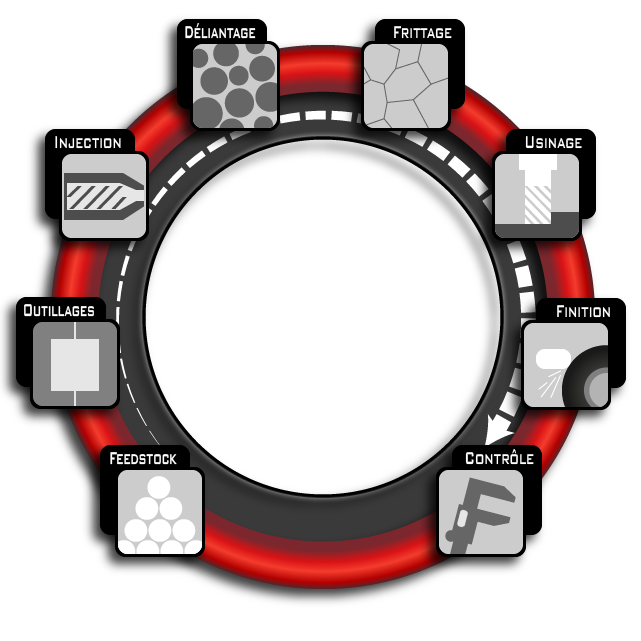
The first process stage consists in shaping the feedstock into parts though a standard plastic injection moulding machine. The injected part is called a green part. Possible additional operations on the green part.
Moulding does not allow for all types of shaping and is not always suitable for multi-versioning. In order to control costs as much as possible, Alliance-MiM works on the green part before the rest of the process. For example, the injection points can be engraved, micro-drilled or milled at this stage with great efficiency and without burrs.